
SALM Pre Reading
At Apex Medical & Rescue, we are committed to providing individuals with the necessary skills and knowledge to handle emergency situations effectively.
The Safe Administration of Life Saving Medications Course covers a wide range of topics, including:
- Common types of life saving medications
- Patient assessment and monitoring
- Administration of life saving medications through different routes
- Legislation, governance, guidelines and polices of administering medications
During the course candidates will learn about the common types of life saving medication and their potential side effects. They will also learn how to determine a patient’s condition and how to assess, monitor and review the effects of medication once it has been administered.
Our SALM Course is delivered by experienced instructors who have extensive knowledge and practical experience. They will guide participants through hands-on training exercises and simulations to ensure a comprehensive learning experience.
Below is a selection of video links, articles and diagrams we would recommend you read or watch ahead of attending a SALM course. This list is not exhaustive but will give you a good baseline for some of topics that will be covered.
Ross & Wilson Anatomy & Physiology
Free textbook covering anatomy & physiology in health and illness.
Primary Survey
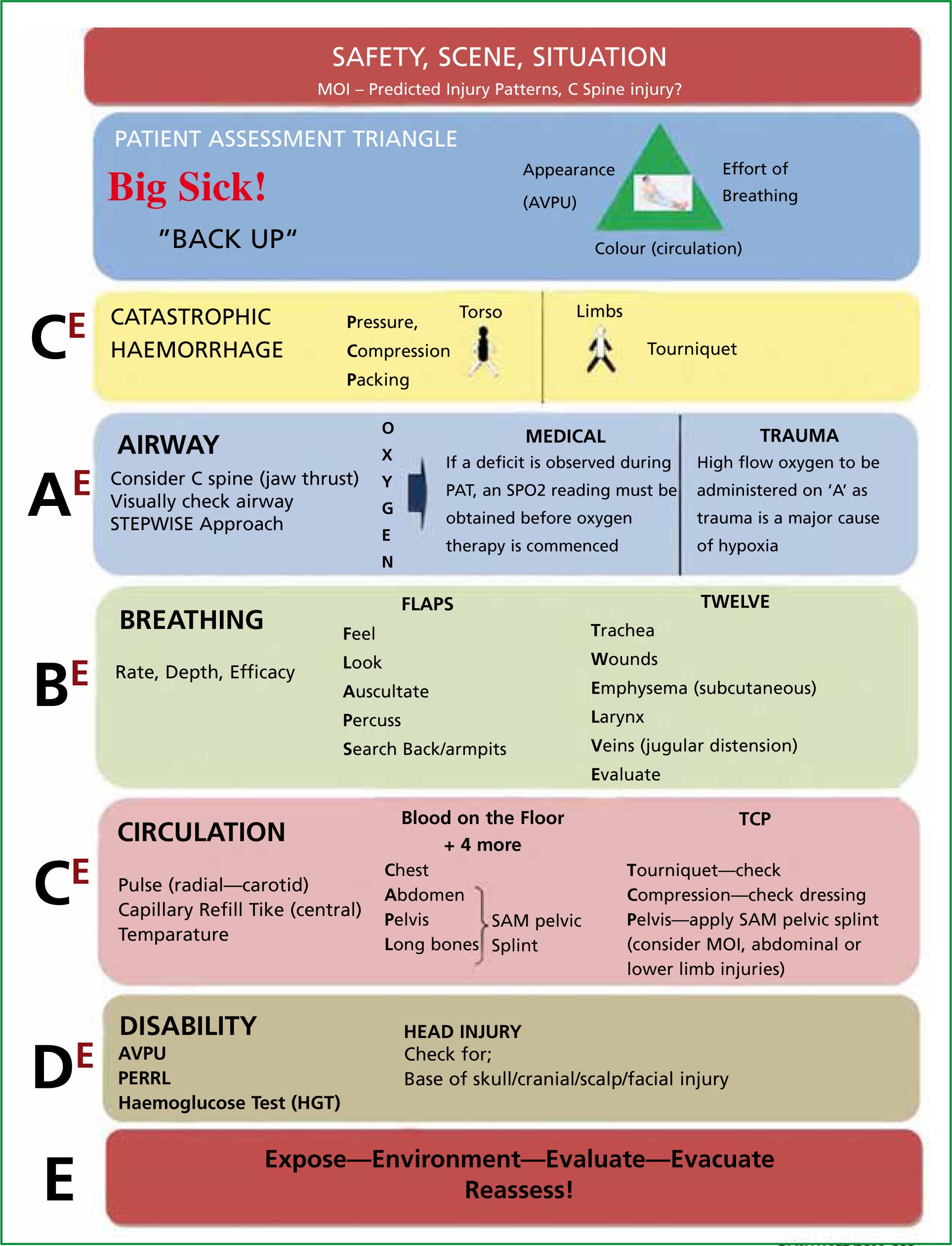

History Taking
-

SAMPLE History Taking Questions
-

SOCRATES Pain History Taking Questions
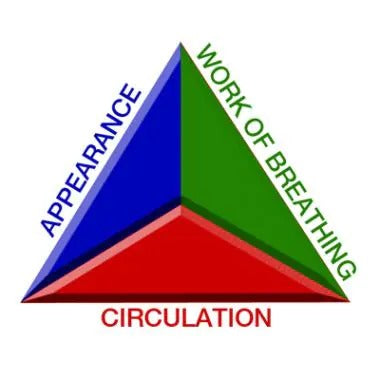
Patient Assessment
Common Medical Conditions
-

-

-

COPD
Watch HereA video explaining chronic obstructive pulmonary disease - emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
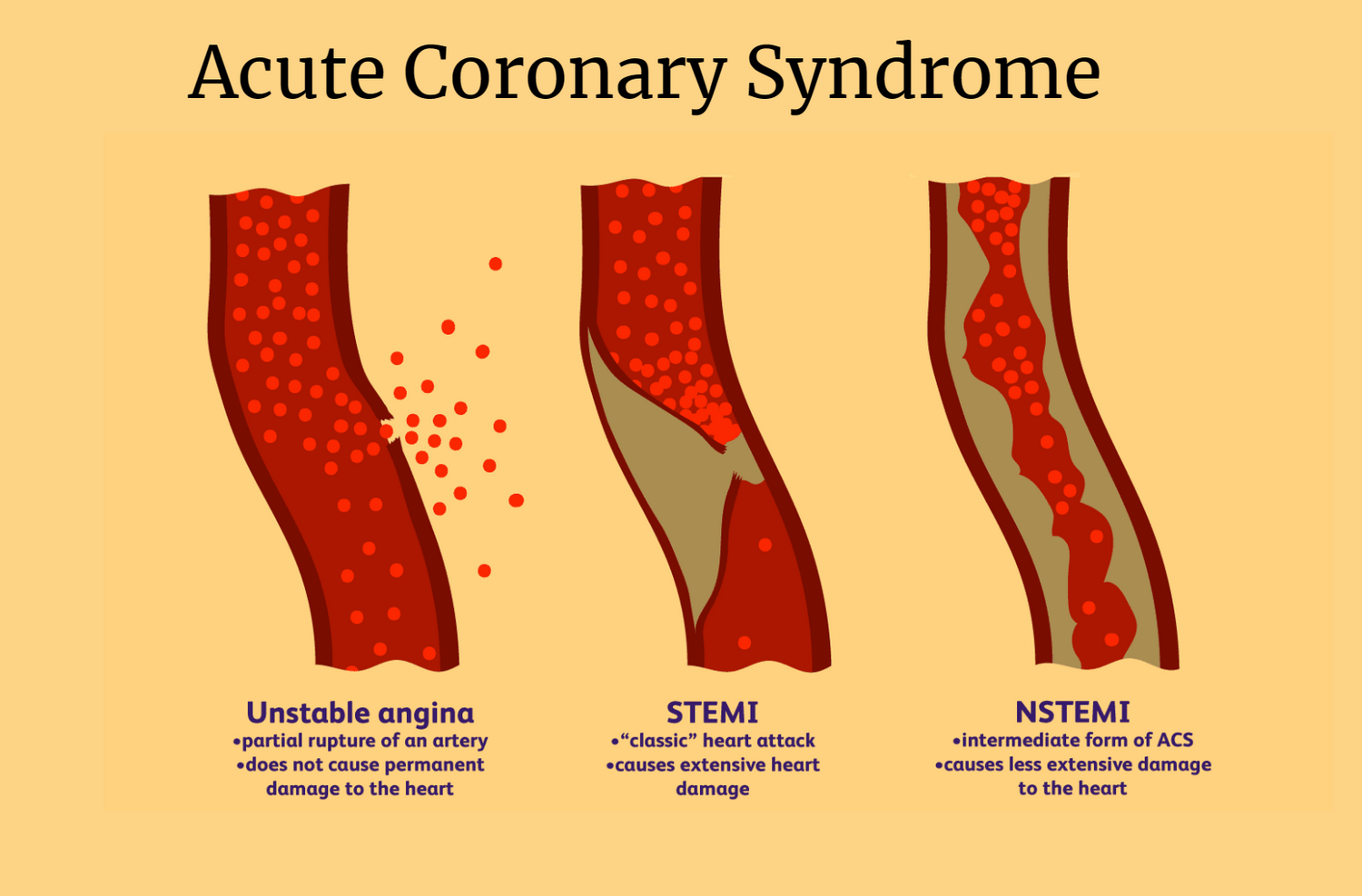
Acute coronary syndrome (ACS) refers to three types of coronary artery disease that affect millions of people each year. It's a medical emergency that can cause unstable angina and heart attack due to artery blockage. With prompt attention, treatment can quickly reopen arteries and help restore blood to your heart, so it can work properly.
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycaemia is a condition in which your blood sugar (glucose) level is lower than the standard range. Glucose is your body's main energy source.
Hypoglycaemia is often related to diabetes treatment. But other drugs and a variety of conditions can cause low blood sugar in people who don't have diabetes.
Medication Legislation

All medicines are controlled by the Medicines Act 1968 and the Human Medicines Regulations (2012). The Medicines Act remains the primary legislation in force and the Human Medicines Regulations updated and clarified this. These set out the requirements for the legal sale, supply and administration of medicines.

Controlled drugs are further governed by legislation including the Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 and the Misuse of Drugs Regulations 2001. The main purpose of these is to prevent the misuse of controlled drugs and covers the prescribing, administering, safe custody, dispensing, record keeping, destruction and disposal of controlled drugs to prevent diversion for misuse.

The Health and Social Care Act 2008 requires all providers of 'regulated activities' in England to register with the Care Quality Commission ( CQC ), and to comply with the requirements and fundamental standards set out in regulations made under that Act.

The Hazardous Waste (England & Wales) Regulations 2005 is a regulatory framework that governs the management and disposal of hazardous waste in England and Wales. The regulations aim to protect human health and the environment by ensuring the proper handling, transport, and disposal of hazardous waste.
Administering Medication

Medication Routes
Medicines vary in form and can be given by a number of different routes. The form and route by which they are given will depend on: the effect required, how the person’s body is able to absorb the medicine, the person’s ability to take the medicine and the forms in which the prescribed medicine is available. The most common routes of administration that you are likely to come across are: oral, nasal, intramuscular injections, nebulisers and inhalation.
Adverse Reaction/Allergies
This is a negative reaction to a medication and can be either mild or very serious (anaphylactic shock), but will not occur in every person taking that medication or on every occasion. You must always check for known adverse reactions or allergies prior to administering medication. If you witness an adverse reaction you must record this.
Side Effects
Medicines are used because we want to produce a specific effect on or within the body. However, they can also produce unwanted effects. These are known as ‘side effects’. What this means is that during the use of the medicine, a potentially harmful or unintended response is created within the body. Common side effects for medicines taken internally involve the gastrointestinal system. For medicines used externally, skin irritation is a common complaint. It is essential that you are aware of the common side effects of the medications you give.

Contraindications & Cautions
A contraindication is a specific situation in which a medicine, procedure, or surgery should not be used because it may be harmful to the person. A caution means that it is possible that the remedy may not be recommended in some circumstances, it is not as strong as a contraindication.









